Computer System Functions: Complete Beginner’s Guide with Examples
Published: 5 Aug 2025
Ever wondered how your computer handles streaming videos, assignments, and chatting all at once? The secret lies in understanding computer system functions. If terms like “input,” “processing,” and “data storage” sound confusing, don’t worry—these concepts are simpler than you think!
In this guide, we’ll explore the 15 essential functions of computer systems with easy-to-understand explanations and practical examples. You’ll learn the four basic functions (input, processing, output, storage) plus modern capabilities like AI processing, connectivity, and automation. Let’s explore computer functionality!
What is a Computer System?
A computer system is a combination of hardware and software working together to perform tasks. Hardware includes physical parts like CPU, memory, and storage devices. Software includes programs and operating systems that give instructions to hardware.
Understanding these functions helps you use computers better and solve basic problems when they occur.
15 Functions of the Computer System
Computer systems perform various essential functions to process information and serve users effectively. These functions range from basic input/output operations to complex data management and security protocols. Understanding these functions helps us appreciate how computers work internally and manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
Core Functions (Traditional 4)
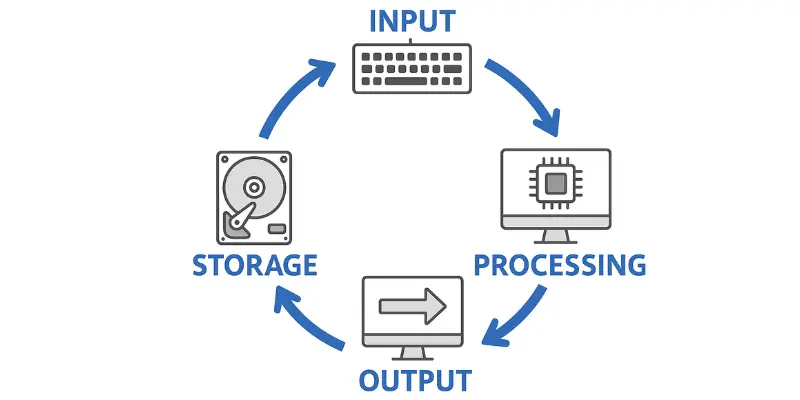
The core functions represent the fundamental operations that every computer system must perform to be functional. These four traditional functions form the foundation of all computer operations and have remained consistent since the early days of computing. They work together in a cycle to transform raw data into meaningful information that users can understand and utilize.
1. Input Function
The input function allows computers to receive data from users. This happens through input devices like keyboard, mouse, touchscreen, microphone, and camera. When you type or click, you’re giving input to the computer.
Example: When you type a message on WhatsApp, the keyboard sends your text as input data to the phone, which then processes and displays it.
2. Processing Function
The processing function is handled by the CPU (Central Processing Unit). The CPU takes input data and transforms it into useful information through calculations and logical operations. This happens very quickly – millions of operations per second.
Example: When you use a calculator app, the CPU processes the numbers you enter and gives you the correct answer instantly.
3. Output Function
The output function presents processed information in formats we can understand. This includes displaying text on screen, playing sounds through speakers, or printing documents. The computer converts its internal data into human-readable form.
Example: When you watch a YouTube video, your computer outputs visual information to your screen and audio to your speakers at the same time.
4. Storage Function
Storage function saves data for future use. Computers use different types of storage: RAM for temporary storage and hard drives or SSDs for permanent storage. Cloud storage lets you save files online and access them from anywhere.
Example: When you save a Word document, it goes from temporary memory (RAM) to permanent storage (hard drive) so you can open it later.
Extended Functions (Modern Applications)
Extended functions represent the advanced capabilities that modern computer systems have developed beyond the traditional four core functions. These functions have emerged due to technological advancement, networking requirements, and the need for sophisticated data management in today’s digital world. They enable computers to perform complex operations, maintain security, and provide seamless user experiences in our interconnected environment.
5. Communication Function
Communication function connects your computer to other devices and the internet. This enables email, video calls, file sharing, and web browsing. Your computer uses Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular connections to communicate.
Example: Video calling on Zoom uses communication functions to send your voice and image to other people in real-time.
6. Control and Coordination Function
This function manages how different computer parts work together. It schedules tasks, allocates memory, and ensures all components operate smoothly without conflicts.
Example: When you run multiple apps, this function decides which app gets CPU time and memory to prevent crashes.
7. Security Function
Security function protects your computer from viruses, hackers, and data theft. It includes antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, and user authentication to keep your information safe.
Example: When you enter a password, security functions verify your identity before allowing access to your files.
8. Automation Function
Automation function performs repetitive tasks automatically without manual intervention. This includes automatic updates, scheduled backups, and smart adjustments based on usage patterns.
Example: Your computer automatically updates software and backs up files while you sleep, ensuring everything stays current and safe.
9. Multimedia Processing Function
Multimedia function handles audio, video, and graphics processing. It enables streaming, gaming, photo editing, and creative applications by processing different types of media simultaneously.
Example: Playing a video game requires processing graphics, sound effects, music, and user inputs all at the same time.
10. Artificial Intelligence Function
AI function enables computers to learn patterns, make predictions, and perform intelligent tasks. This includes voice recognition, image analysis, and smart recommendations.
Example: When you ask Siri a question, AI functions understand your speech, process the meaning, and provide relevant answers.
11. Internet of Things (IoT) Function
IoT function connects computers to smart devices like home appliances, sensors, and wearables. This creates networks of connected devices that share information and work together.
Example: Smart home systems use IoT functions to control lights, temperature, and security cameras from your smartphone.
12. Virtualization Function
Virtualization function creates virtual versions of hardware resources, allowing multiple operating systems or applications to run on one physical computer.
Example: Using virtual machines to run Windows on a Mac computer, or running multiple test environments for software development.
13. Backup and Recovery Function
Backup function automatically saves copies of essential data to prevent loss. Recovery function restores data when problems occur, like accidental deletion or system crashes.
Example: Google Photos automatically backs up your phone pictures to the cloud, so you don’t lose them if your phone breaks.
14. User Interface Function
User interface functions create the visual elements and interactions that enable humans to use computers easily. This includes windows, icons, menus, and touch gestures.
Example: The desktop, apps icons, and touch gestures on your smartphone are all part of the user interface function.
15. Performance Monitoring Function
Performance monitoring function tracks how well your computer is running. It monitors CPU usage, memory, storage space, and identifies problems before they cause crashes.
Example: Task Manager on Windows shows which programs are using the most resources and helps you close problematic applications.
How These Functions Work Together
All 15 functions operate simultaneously to create a smooth user experience. When you open a video file, input receives your click, processing analyzes the file, storage retrieves data, output displays the video, and security ensures safe operation – all happening in milliseconds.
Real-World Applications
Education: Online learning platforms, interactive simulations, and collaborative tools for remote learning.
Business: Inventory management, global communication, data analysis, and automated customer service.
Healthcare: Patient monitoring, diagnostic imaging, telemedicine, and electronic health records.
Entertainment: Video streaming, gaming, music production, and social media platforms.
Future of Computer Functions
Emerging technologies will enhance current functions and add new capabilities. Quantum computing will provide massive processing power, while enhanced AI will make automation smarter and more responsive.
New input methods like brain-computer interfaces and advanced output through virtual/augmented reality will create more immersive experiences.
Conclusion
Understanding computer system functions opens up a new perspective on everyday technology. From basic functions—input, processing, output, and storage—to advanced capabilities like AI and automation, computers have evolved into sophisticated machines shaping our world. These 15 functions work together seamlessly. When you send a message or play a game, multiple functions activate simultaneously—processing input, accessing data, connecting to networks, and delivering output—all within milliseconds.
As technology advances with quantum computing and enhanced AI, these core functions remain the foundation. For students, grasping these concepts provides practical knowledge for better technology decisions and problem-solving. Next time you use any device, you’ll recognize these functions in action. You’re no longer just a user—you understand the engineering behind modern digital experiences.
Keep exploring and learning!
The main functions are input, processing, output, and storage. These four work together to receive data, transform it, present results, and save information.
Modern computers perform 15 essential functions, including basic operations and advanced capabilities like AI, security, and automation.
Processing is crucial because it transforms raw data into useful information. However, all functions are important and work together.
Input receives data from users, while output presents processed results. Together they create interactive experiences where actions produce immediate responses.
Processing actively transforms data, while storage preserves data for future use. Processing is temporary work, storage is permanent saving.
AI has made automation smarter, improved user interfaces with voice control, and enabled predictive capabilities for better performance.
Students should understand basic functions plus AI processing, internet connectivity, cybersecurity, multimedia handling, and automation.
They enable communication, entertainment, work, and education by automating tasks, connecting us globally, and providing creative tools.
Future includes quantum processing, enhanced AI, better human-computer interfaces, and seamless device connectivity.
Practice with different software, take computer courses, experiment with programming, and stay updated with technology trends.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks