Hard Disk Parts Explained: From Platter to Power Connector
Published: 26 Jul 2025
A computer includes many essential components. Each part plays a different role to ensure the device operates normally. The hard disk is a crucial component for storing data in a computer, particularly long-term memory, allowing users to save and access files even when the computer is shut down. Without a hard disk, you cannot store your data permanently. So, we will provide you with necessary information about all parts of the hard disk and their functions, along with the operating principle of the hard disk in this article.
What is a Hard Disk in a Computer?
A hard disk, also known as a hard disk drive (HDD), is a storage device used in many electronic devices, especially computers, to store and retrieve digital data. The hard disk offers a large capacity to save documents, particularly hundreds of gigabytes. It is also very portable, as it can be removed and used on any compatible device. To have a nearly perfect hard disk like we do today, it has been upgraded continuously for over 50 years, particularly:
From 1953 to the 1970s: IBM developed and released the first HDD for low-cost random access storage, with small storage capacity and bulky design—3.75 MB of data and the size of a fridge, respectively.
1980s: Developers optimized the size of HDDs, down to 2.5 and 3.5 inches, and also upgraded the storage to megabytes.
From 2007 to 2012: Hitachi Global Storage Technology (HGST) published the first 1TB HDD and increased durability by using helium in 2012.
2015: HGST introduced the first 10TB HDD.
2018: Western Digital launched the Purple 12TB with AI-powered technology.
2021: Western Digital released two 20TB HDDs for business use—Ultrastar DC HC560 and WD Gold HDD Enterprise Class SATA HDD.
2025: Seagate introduced a 36TB HDD using modern technologies like HAMR and MAMR.
Internal Components of a Hard Disk
A hard disk contains several internal parts that work together to read, write, and store your data efficiently. Below are the key components found inside a typical hard disk drive.
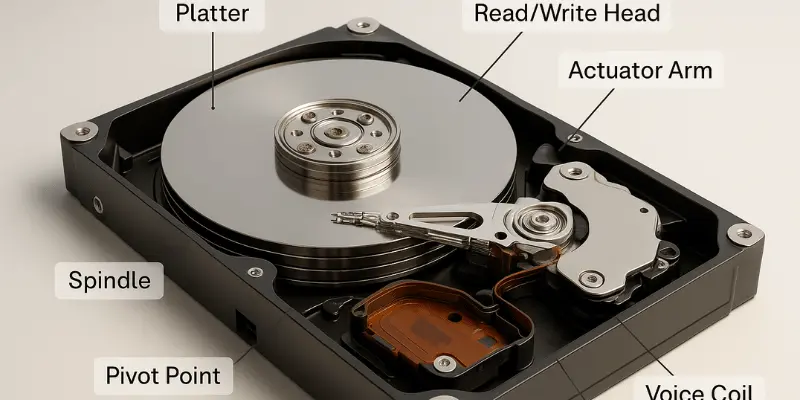
1. Platter(s)
The platter is a circular part made from magnetically neutral materials such as aluminum or glass to store data. The manufacturer covers the surface with a thin magnetic layer (10 to 20 nanometers), which helps this part store all data. The magnetic layer is vulnerable and easily damaged physically, so there is a protective layer made of durable material like carbon to shield it from accidents. There are also many types of platters with different sizes and capacities to fit various devices. A larger size tends to have a larger capacity.
2. Spindle
The spindle acts like the engine of the hard disk; this part ensures the operation of the platter by rotating it at high speeds (e.g., 5400 RPM, 7200 RPM, or higher). Platters are placed on a hub of a spindle and are kept fixed while the spindle rotates, which affects data access speed and drive performance.
3. Read/Write Head
To read and write data to the platters, there is a tiny disk drive component positioned above and below each platter surface. These heads are responsible for changing the magnetization of the platter’s surface to process data. The distance between the head slider and the platter is very thin—just about 5–10 nanometers. In addition, it is very important to clean the read/write head because if any dust detaches from it, it will affect the processing elements inside, and the head will be damaged.
4. Actuator
The actuator, also known as the read/write arm, receives instruction signals from the drive’s circuit board to control and move back and forth across the platters. This movement ensures exact data transfer and accurate placement of the read/write heads. There is also a Voice Coil Actuator, which responds quickly and uses electromagnetic force to move the read/write arm to the required location. The coordination between the Voice Coil Actuator and the read/write arm ensures smooth and efficient data processing.
External Components of a Hard Disk
In addition to internal parts, a hard disk also has external components that protect it and help it connect with your computer. Let’s explore the main external parts of a hard disk.
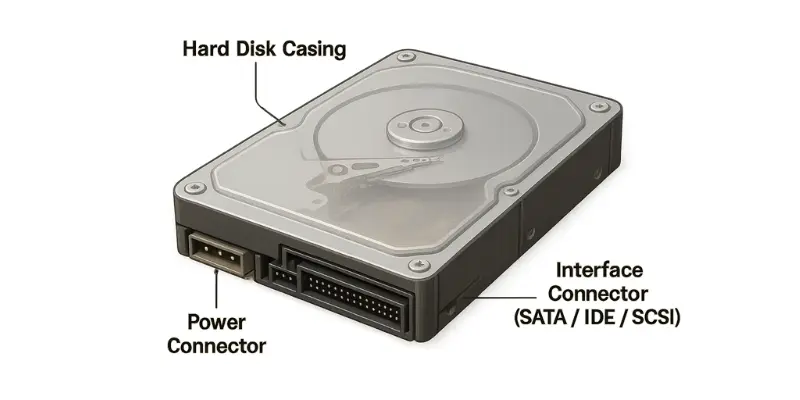
1. Hard Disk Casing
The case of the hard disk is responsible for holding all the components together. It is made of metal to ensure durability. Besides helping to prevent physical damage, the case also protects components from dust or electromagnetic interference.
2. Interface Connector
To transfer data between a hard disk and a computer, each disk is equipped with an interface connector—a physical port that links the HDD to the motherboard. There are various connector types like SATA (Serial ATA), IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics), and SCSI (Small Computer System Interface), each with different configurations. Particularly, SATA and IDE are older models known for their stability and durability, while SCSI is a modern interface that helps optimize the performance of your devices.
3. Power Connector
The power connector supplies electrical power to the hard drive to spin the platters and operate the actuator. It is one of the most crucial parts of the HDD, ensuring the entire device operates properly. In some HDD models, the power connector and the interface connector are combined into one cable, simplifying the design while maintaining performance.
How These Parts Work Together
A hard disk works by processing data from computers or other technology devices, helping store documents even when the device is turned off. All your data is saved in tiny magnetic regions on the platter, which spins at high speed by the spindle. When you request to access any data, the hard disk identifies the specific region on the platter and operates to retrieve the exact information. The entire process involves all the components of the hard disk drive and requires perfect interaction between them.
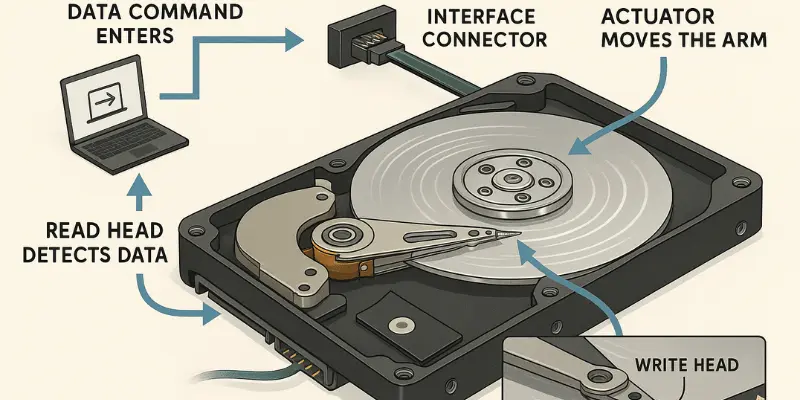
Here is a step-by-step overview of what happens when the computer processes data:
The computer sends a command to the hard disk through the interface connector.
The actuator moves the read/write head and adjusts it to the correct position on the spinning platter.
The read head detects the magnetic signal of the bits and converts it into electrical signals.
When writing, the write head changes the magnetic orientation to represent new data.
This entire process happens within milliseconds and is repeated thousands of times per second to ensure the computer runs smoothly.
Conclusion
The hard disk is the foundation of computer storage technology and plays a vital role in storing data. By utilizing magnetic technology, hard disks provide an effective method of saving data and help reduce operating costs. Despite their physical complexity, the absolute precision of hard disks makes them highly reliable for both personal and business use. A hard disk is not just a storage device—it is a bridge connecting our real life to the digital world.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks