Parts of a Computer Keyboard Explained: A Beginner-Friendly Guide
Published: 4 Aug 2025
The components of a computer keyboard are vital for your overall experience, whether you’re working on assignments or gaming. However, many users are unaware of how each part impacts performance and comfort. If you’re struggling with slow responses or discomfort while typing, this guide breaks down the essential keyboard components, how they work, and their impact on your experience. Whether you’re a student or a gamer, understanding these parts can improve your performance and comfort.
What is a Keyboard Made Of?
A computer keyboard is made up of several key components that work together to provide a seamless typing experience. Understanding these parts helps users choose the right keyboard based on their needs, whether for gaming, typing, or general use. Let’s break down the components of a computer keyboard and how each part contributes to the overall performance.
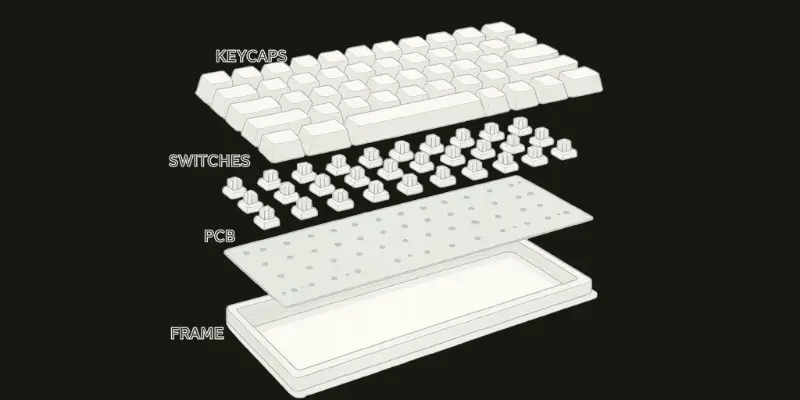
What are the Parts of the Keyboard?
A keyboard is made up of many parts of a computer keyboard, each with a specific function. These parts range from the switches that detect keystrokes to the frame that holds everything together. Let’s look at each key element that makes up a keyboard’s parts name.
- Key Switches
- Keycaps
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
- Stabilizers
- Case/Frame
- Backlighting
- Microcontroller
- Wiring or Wireless Transmitter
- Switch Mounting
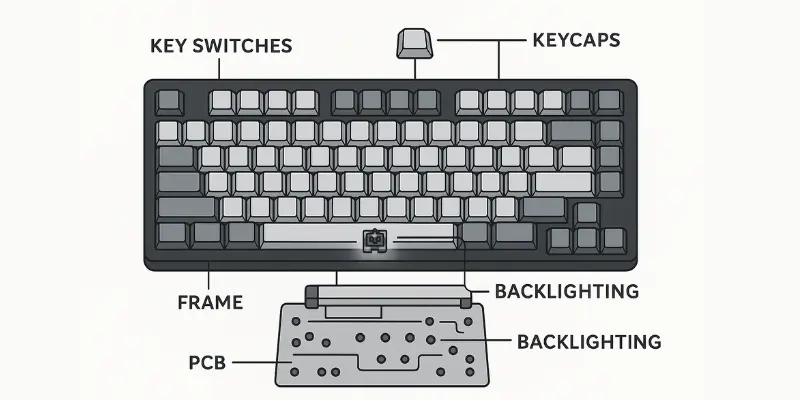
1. Key Switches
Key switches are at the heart of a keyboard. These are the mechanisms beneath each key that detect when a key is pressed. There are two main types: mechanical and membrane. Mechanical switches offer tactile feedback and are preferred for their durability and response time, making them ideal for gamers and typists who need quick and precise input. Membrane switches, on the other hand, are quieter and generally cheaper but may lack the same responsiveness and longevity.
2. Keycaps
Keycaps are the plastic covers that sit on top of the switches. The material and shape of keycaps play a significant role in your comfort and typing experience. Common materials include ABS (softer but less durable) and PBT (sturdier and longer-lasting). The shape of keycaps, like concave or cylindrical, can impact how your fingers feel while typing, especially during long sessions.
3. PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
The PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is the backbone of a keyboard, connecting all the switches to the computer. When a key is pressed, the PCB registers the keystroke and sends the signal to the computer. Some keyboards feature hot-swappable PCBs, allowing users to change switches without soldering, while others are non-hot-swappable, requiring more technical skill to modify.
4. Stabilizers
Stabilizers are important for larger keys like the spacebar, enter, and shift. These parts ensure that the keys press evenly, preventing wobbling and creating a more stable and consistent typing experience. Stabilizers can be found in mechanical and membrane keyboards and help maintain uniformity in the feel of the keys.
5. Case/Frame
The case or frame holds the internal components of the keyboard together, providing structure and durability. It can be made from materials such as plastic, aluminum, or steel, each contributing differently to the weight, sound, and feel of the keyboard. The case design can also affect the acoustics of key presses, creating a more solid or hollow sound depending on the material.
6. Backlighting
Backlighting illuminates the keys, which can be especially useful in low-light conditions. Many keyboards feature RGB backlighting, which allows for customizable colors, making it ideal for gamers who want to add a personal touch. Single-color backlighting is a more basic option, often used for practical purposes and less focused on aesthetics.
7. Microcontroller
The microcontroller is the brain of the keyboard. It’s a small chip that processes all the input data from the switches and sends it to the computer. The microcontroller is essential for ensuring that each keystroke is registered correctly and that the keyboard responds to your actions in real time.
8. Wiring or Wireless Transmitter
A keyboard can either be wired or wireless, depending on how it connects to your computer. Wired keyboards use cables to transmit signals, offering a more reliable connection with less interference. Wireless keyboards use Bluetooth or RF signals, offering more freedom but sometimes suffering from minor latency or interference.
9. Switch Mounting
Switch mounting refers to how the switches are secured within the keyboard. Common mounting styles include top-mount, tray-mount, and sandwich-mount, each affecting the overall feel and sound profile of the keyboard. Top-mounted switches tend to offer a softer feel, while tray-mount setups can produce a more rigid typing experience.
4. Choosing the Right Keyboard
When deciding on a keyboard, it’s important to consider your specific needs. For students, comfort and quiet typing are key. A keyboard with membrane switches and an ergonomic layout would be ideal for long study sessions. On the other hand, gamers will benefit from a keyboard with mechanical switches that offer fast response times and durability. Key switches with tactile feedback and customizable backlighting are also highly recommended for a premium gaming experience.
5. Customization and Care
One of the great things about modern keyboards is their ability to be customized. You can easily swap out keycaps, change switches, or adjust backlighting to suit your personal style. Maintenance is equally important—regular cleaning of your keyboard will ensure longevity and smooth performance. Be sure to clean your key switches and keycaps regularly to avoid dust buildup, and always take care of your keyboard’s wiring or wireless connection to maintain a fast, responsive experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the parts of a keyboard is key to improving your typing experience, whether you’re a student working through assignments or a gamer striving for precision in every keystroke. We’ve explored the essential components of a keyboard, from key switches and keycaps to the underlying circuitry that powers your typing. Each part serves a unique function, and knowing how they work together can help you make more informed decisions when choosing or customizing a keyboard for your needs. Whether you’re seeking better comfort, faster typing, or enhanced gaming performance, the right keyboard components can make all the difference.
The five main parts of a keyboard are:
- Key Switches – The mechanisms beneath each key that register your keystrokes and send signals to the computer. They determine the typing feel, speed, and sound.
- Keycaps – The plastic covers you press when typing. They come in different materials and shapes, affecting comfort and durability.
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board) – The electronic board inside the keyboard that connects all switches and transfers your keystroke signals to the computer.
- Stabilizers – Small support components under larger keys (like the spacebar, enter, and shift) that ensure smooth and balanced key presses.
- Case/Frame – The outer shell that holds all the keyboard parts together, providing structure, durability, and affecting the typing sound.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks