A Simple Guide to the 10 Types of Computers and Their Uses
Published: 16 Aug 2025
When Alan Turing built one of the first modern computers in the 1940s, it filled an entire room and could only solve a handful of problems. Today, computers come in all shapes and sizes — from supercomputers that can predict hurricanes to the tiny chips inside your smartwatch.
Think about your daily life. You might start your morning checking emails on a laptop, stream music on your phone, and later drive a car that uses embedded computers to keep you safe. Each of these is a different type of computer, designed with a specific job in mind.
In this guide, we’ll explore the main types of computers, explain how they work, and share real-life examples so you can easily tell them apart. Whether you’re a student, a tech lover, or just curious, you’ll get a clear, simple breakdown — without any confusing jargon.
What Are the Types of Computers?
Computers come in many shapes, sizes, and capabilities. From tiny devices that fit in your hand to massive machines that fill entire rooms, each type serves a unique purpose. Understanding the different types of computers helps you know which one is right for your needs — whether it’s for personal use, business, research, or entertainment. In fact, there are many categories of computer systems, each designed for specific tasks.
Here are the 10 main types of computers:
- Supercomputer
- Mainframe Computer
- Minicomputer
- Microcomputer (Personal Computer)
- Workstation
- Server Computer
- Laptop
- Tablet
- Smartphone
- Wearable Computer
Let’s explore all these types in detail and see how they work in real life.
1. Supercomputers
A supercomputer is the fastest and most powerful type of computer in the world. It can handle problems so complex that a normal computer might take months or even years to solve them, while a supercomputer can do the same job in just seconds. These machines are built with thousands, and sometimes millions, of processors that work together to perform trillions of calculations every second. Among the different types of computers, supercomputers stand out for their unmatched speed and processing power.
Key features of Supercomputers
- Designed for extreme speed, accuracy, and efficiency in handling large amounts of data
- Capable of performing trillions of calculations per second
- Runs advanced simulations and processes massive datasets in real time
- Uses thousands or millions of processors working together
- Built for specialized, complex tasks rather than everyday computing
Examples and Uses of Supercomputers
- Predicting weather patterns and tracking hurricanes
- Studying diseases and developing medical solutions
- Exploring space and simulating astronomical events
- Running advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning programs
- Examples include Fugaku (Japan), Summit (USA), and Frontier (one of the fastest in the world)

2. Mainframe Computers
A mainframe computer is a large and powerful machine mainly used by big organizations to handle huge amounts of data. Unlike personal computers, mainframes are designed to process and store information for hundreds or even thousands of users at the same time. They are one of the oldest types of computers still in use today, valued for their reliability and long-term performance.
Key features of Mainframe Computers
- Can run multiple programs and handle many users at once
- Designed for stability, durability, and continuous operation
- Processes large-scale data quickly and securely
- Often works with specialized operating systems
- Requires skilled staff for maintenance
Examples and Uses of Mainframe Computers
- Banking systems for handling millions of daily transactions
- Airline reservation systems
- Government databases and census data processing
- Healthcare records and insurance systems
- Examples include IBM Z series and Unisys ClearPath systems

3. Minicomputers
A minicomputer is smaller than a mainframe but more powerful than a personal computer. It is built to serve multiple users at once, making it ideal for small to medium-sized businesses. These computers became popular in the mid-20th century for their balanced performance and size.
Key features of Minicomputers
- Supports multiple users at the same time
- Mid-range processing power and storage capacity
- Smaller size compared to mainframes
- Flexible and adaptable for different industries
- Can be networked to share resources
Examples and Uses of Minicomputers
- Factory automation and industrial control
- Small business data management
- University research labs
- Scientific simulations
- Examples include DEC PDP series and IBM AS/400

4. Microcomputers (Personal Computers)
A microcomputer, also called a personal computer (PC), is the most common type of computer used at home and in offices. It is designed for individual use and can handle everyday tasks like browsing the internet, typing documents, and playing games.
Key features of Microcomputers
- Compact and affordable
- Designed for single-user operation
- Can run a variety of software programs
- Comes in desktop and laptop versions
- Easy to upgrade and customize
Examples and Uses of Microcomputers
- Office work like word processing and spreadsheets
- Internet browsing, gaming, and multimedia
- Educational purposes in schools and colleges
- Small business accounting and inventory management
- Examples include Dell, HP, Lenovo, and Apple Mac computers

5. Workstations
A workstation is a high-performance computer designed for professional work. It offers more power than a regular PC and is built for tasks that need speed, precision, and reliability.
Key features of Workstations
- High processing power and graphics capabilities
- Suitable for heavy software like CAD, 3D rendering, and video editing
- Often includes error-correcting memory for stability
- Can handle large files and complex calculations
- Built for long hours of continuous operation
Examples and Uses of Workstations
- Animation and 3D modeling
- Architectural design
- Scientific research and simulations
- Video production and editing
- Examples include HP Z series and Dell Precision

6. Servers
A server is a computer that provides services, data, or programs to other computers over a network. It is built to run continuously and serve multiple clients at once.
Key features of Servers
- Operates 24/7 without interruption
- Manages resources for multiple users
- Can store and deliver data, files, and applications
- Built for security and stability
- Often housed in data centers
Examples and Uses of Servers
- Hosting websites and applications
- Email and file sharing services
- Company intranets
- Online gaming platforms
- Examples include Dell PowerEdge and HP ProLiant

7. Laptops
A laptop is a portable computer that combines all the features of a desktop in a compact, foldable design. It runs on a rechargeable battery, making it ideal for people who work on the go.
Key features of Laptops
- Lightweight and easy to carry
- Built-in screen, keyboard, and touchpad
- Runs on battery and can be plugged in when needed
- Comes in various sizes and performance levels
- Can connect to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other devices
Examples and Uses of Laptops
- Business presentations and remote work
- Online learning and research
- Gaming and entertainment
- Creative tasks like writing, graphic design, and video editing
- Examples include MacBook, Dell XPS, and Lenovo ThinkPad

8. Tablets
A tablet is a slim, lightweight computer with a touchscreen. It is smaller than a laptop but bigger than a smartphone, offering portability and ease of use.
Key features of Tablets
- Touchscreen interface without a physical keyboard
- Lightweight and battery-powered
- Ideal for browsing, reading, and multimedia
- Can run apps for work and entertainment
- Supports stylus input for drawing and note-taking
Examples and Uses of Tablets
- Digital textbooks and e-learning
- Watching videos and browsing the internet
- Sketching and graphic design
- Video calls and online meetings
- Examples include Apple iPad, Samsung Galaxy Tab, and Microsoft Surface

9. Smartphones
A smartphone is a handheld computer that combines the features of a phone with internet access, apps, and multimedia capabilities.
Key features of Smartphones
- Portable and fits in your pocket
- Touchscreen with virtual keyboard
- Runs mobile operating systems like Android or iOS
- Access to millions of apps
- Built-in camera, GPS, and sensors
Examples and Uses of Smartphones
- Making calls and sending messages
- Browsing the internet and social media
- Navigation and GPS tracking
- Mobile gaming and streaming
- Examples include iPhone, Samsung Galaxy, and Google Pixel

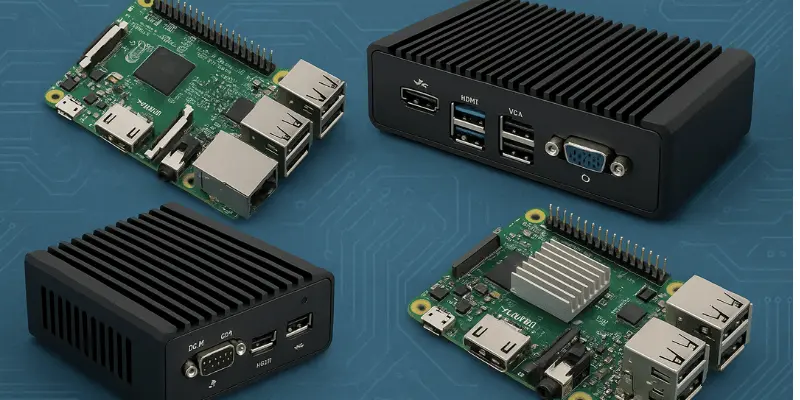
10. Embedded Computers
An embedded computer is a small computer built into a larger device to perform specific tasks. It is not meant for general use but for controlling the functions of the device it’s inside.
Key features of Embedded Computers
- Small and task-specific
- Low power consumption
- Works without user intervention
- Highly reliable and durable
- Runs on custom software
Examples and Uses of Embedded Computers
- Engine control in cars
- Smart appliances like washing machines and microwaves
- Medical devices and monitoring systems
- Industrial machines and robotics
- Examples include Raspberry Pi used in embedded projects

How to Choose the Right Type of Computer for Your Needs
Not every computer is built for the same job. The different type computer you choose should depend on what you need it for:
- For heavy data processing → A supercomputer or mainframe might be the right choice.
- For office or business work → A workstation, server, or desktop PC will be reliable.
- For personal use → Laptops, tablets, or smartphones are perfect.
- For on-the-go use → Wearable computers like smartwatches offer convenience.
When comparing computer different types, always think about your budget, performance requirements, and portability needs.
Conclusion
Computers have become an essential part of our daily lives, and understanding the different types of a computer helps you choose the right one for your needs. From the most powerful supercomputers to the smallest wearable devices, every type serves a unique purpose. These various types of computer systems show how technology has evolved to solve different problems in different ways.
When you explore the 10 types of computers, you see the wide range of capabilities they offer — from data-crunching giants to portable devices we carry in our pockets. By knowing the kinds of computer available today, you can make smarter decisions for work, study, or entertainment.
Also Read this 👇👇👇
8 Different Types of Microphones
10 Types of Computer Keyboards
Discover the Laptop Screen Types
Discover the Different Types of Webcams
10 Types of Speakers and Their Uses
10 Common Types of Computer Viruses
Types of Laptop Chargers Explained
10 Different Types of Computer Mouse
Explore All Laptop Accessory Types
Top 5 Types of Laptop Bags for Students and Professionals
Types of Laptop Battery: Understanding Li-ion, LiPo, & More
10 Types of Laptop Ports | Which Ones Do You Really Need?
Types of Laptop Processors Learn Intel Core, Dual Core, AMD
6 Types of Motherboards Explained – Make the Right Choice!
The fastest computers in the world are supercomputers. They can process trillions of calculations per second, making them perfect for weather forecasting, scientific research, and complex simulations.
No. While both are microcomputers, laptops are portable, and desktops are designed to stay in one place.
For gaming, a high-performance desktop PC or gaming laptop is the best choice. They can handle advanced graphics and fast processing.
Yes. Smartphones are a type of microcomputer because they can store, process, and run software applications just like a traditional computer.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks